
Why care about text?#
Chat bots
Spell checking
Speech recognition
Sentiment analysis
Book recommder
Translators
…

Working with text data#
Algorithms work well with numbers
working with text = meaningfully transforming your data into numbers
meaningful = depends on your application
Converting text into numbers#
this is also called text preprocessing
Text processing → text to numbers#
Local representations
Encoding with a unique number
Statistical Encodings
Distributed Representations
Word Embeddings
Text processing → text to numbers#
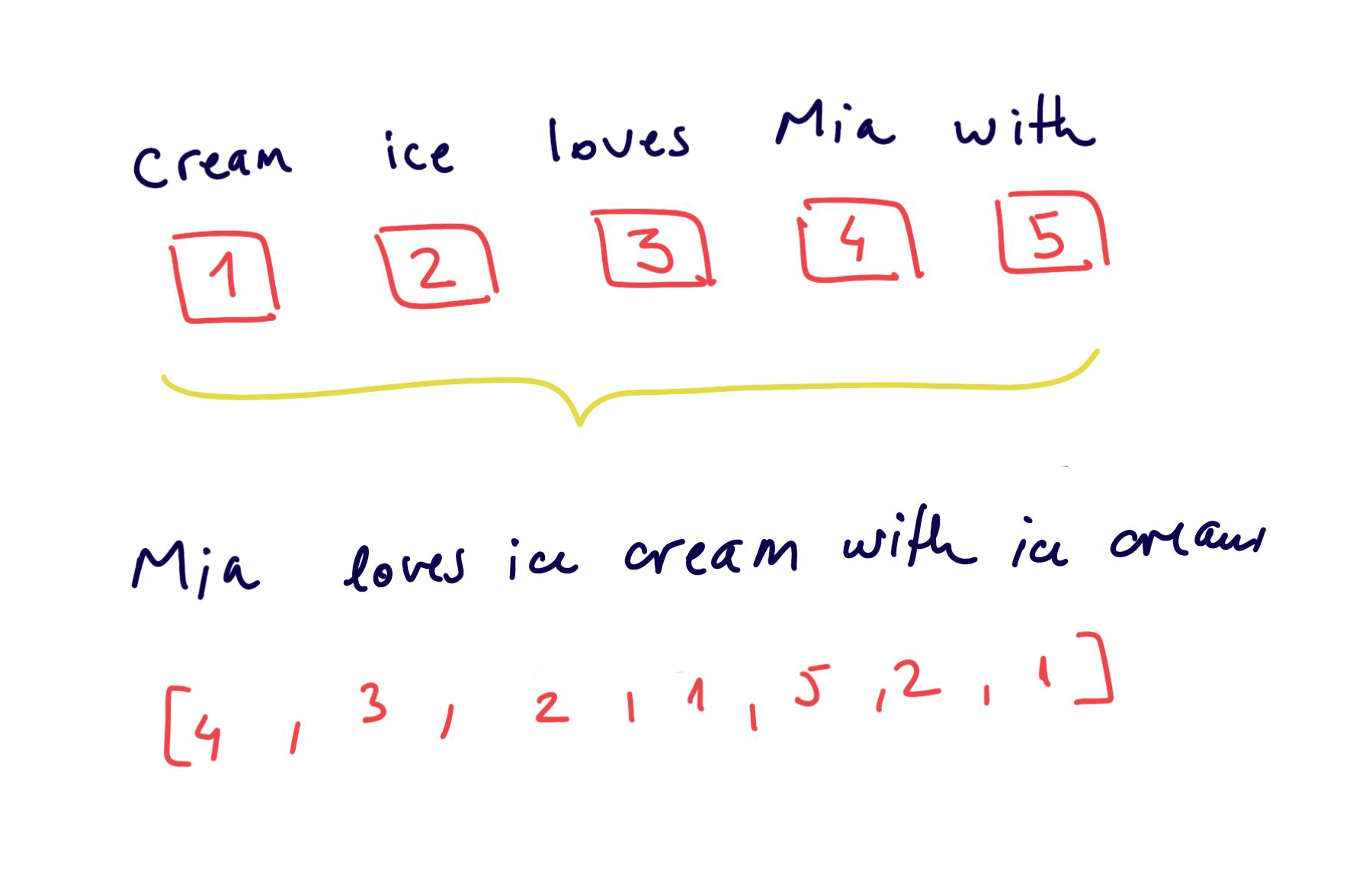
Encoding with a unique number
Easy to create, but the numbers have no relational representation
the relationship between words is not captured
models cannot interpret well these representation
Text processing → text to numbers#
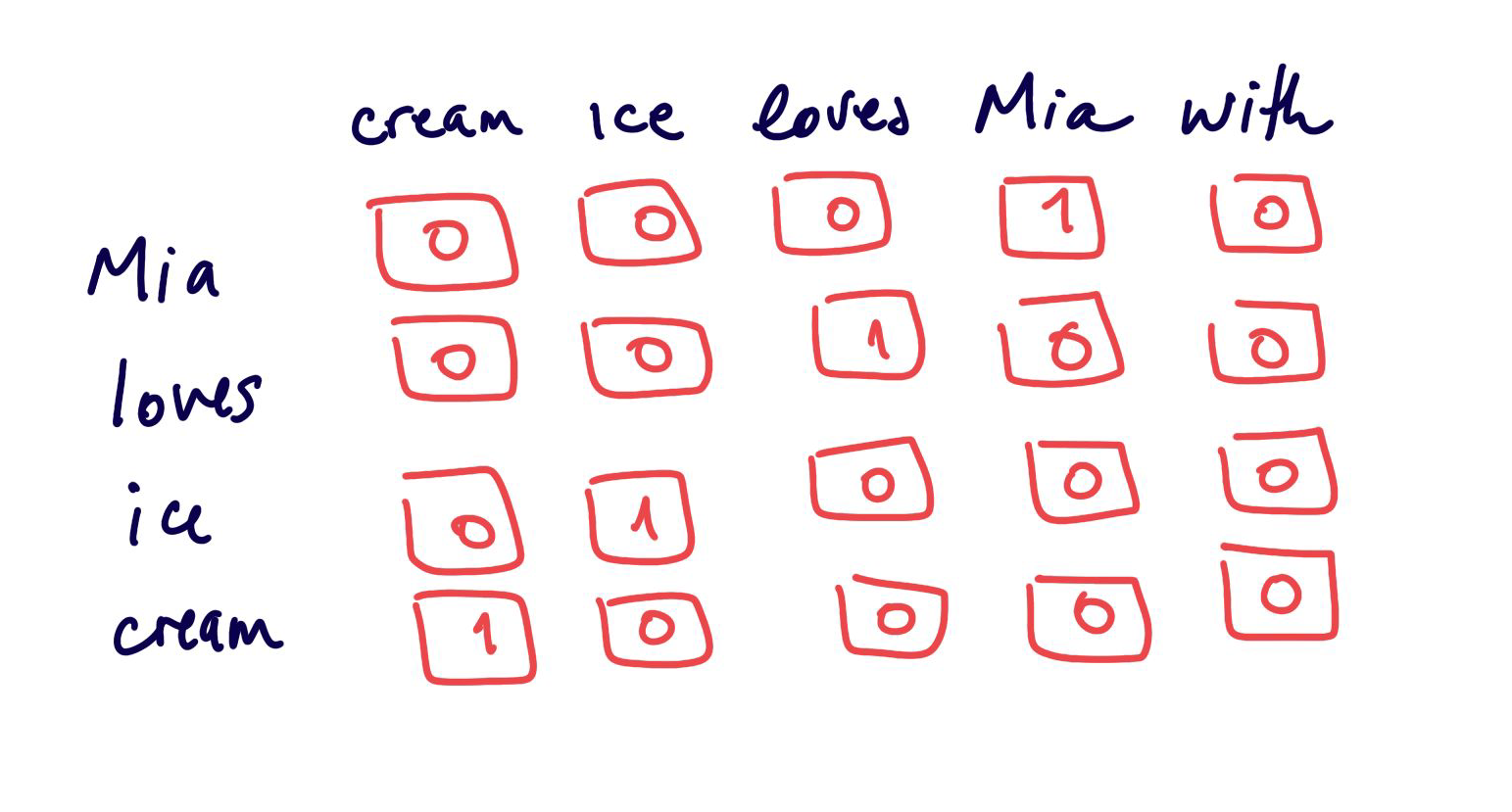
Statistical Encodings
Creating vectors of the size of the vocabulary
leads to large sparse features space
not very efficient
Text processing → text to numbers#
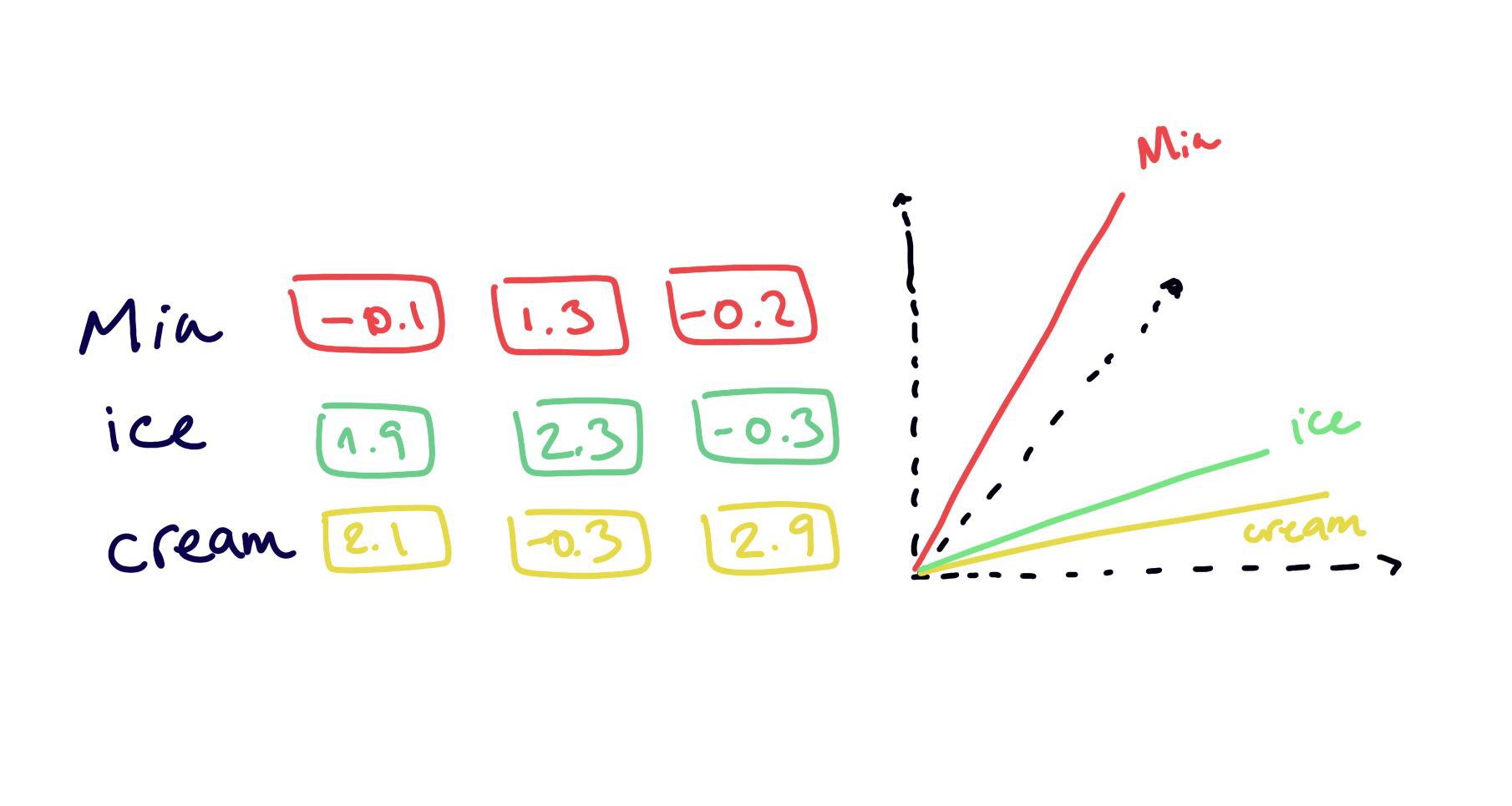
Word Embeddings
embedding = new latent space
properties and relationships between items are preserved
less number of dimensions
less sparseness
Statistical Encodings#
Text Preprocessing#
Tokenization
CountVectorizer
TF-IDF
N-grams
Normalization
Stemming
Lemmatization
Stop Words
Tokenization#

import nltk
nltk.download("punkt")
nltk.download("wordnet")
nltk.download("punkt_tab")
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize, word_tokenize
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer
import pandas as pd
text = "Let us learn some NLP. NLP is amazing!"
word_tokenize(text)
['Let', 'us', 'learn', 'some', 'NLP', '.', 'NLP', 'is', 'amazing', '!']
sent_tokenize(text)
['Let us learn some NLP.', 'NLP is amazing!']
CountVectorizer#
Converting a collection of text documents to a matrix of token counts
CountVectorizer#


Gives a lot of weight to frequent (and maybe not so informative) words… → TF-IDF fixes this
corpus = [
'This is the first Document.',
'This document is the second document.',
'And this is the third one.',
'Is this the first document?'
]
cv = CountVectorizer()
X = cv.fit_transform(corpus)
features = cv.get_feature_names_out()
print(f"Features - {features}")
output = pd.DataFrame(X.toarray(), columns=cv.get_feature_names_out())
print("\n",output)
Features - ['and' 'document' 'first' 'is' 'one' 'second' 'the' 'third' 'this']
and document first is one second the third this
0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1
1 0 2 0 1 0 1 1 0 1
2 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1
3 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
y = ['document 1', 'document 2', 'document 3', 'document 4']
model = LogisticRegression().fit(X, y)
query = ['What is about second document?']
query_transformed = cv.transform(query)
model.predict(query_transformed)[0]
#model.predict_proba(query_transformed)[0]
'document 2'
TF-IDF#
TF-IDF: Term Frequency * Inverse Document Frequency
→ measure how important a word is to a document in a corpus
A frequent word in a document that is also frequent in the corpus is less important to a document than a frequent word in a document that is not frequent in the corpus.
TF-IDF#
TF:
IDF:
TF-IDF:
TF-IDF#


In detail article how Tf-IDF works.
corpus = [
'This is the first Document.',
'This document is the second document.',
'And this is the third one.',
'Is this the first document?',
]
tfidf = TfidfVectorizer()
X = tfidf.fit_transform(corpus)
X.toarray()
array([[0. , 0.46979139, 0.58028582, 0.38408524, 0. ,
0. , 0.38408524, 0. , 0.38408524],
[0. , 0.6876236 , 0. , 0.28108867, 0. ,
0.53864762, 0.28108867, 0. , 0.28108867],
[0.51184851, 0. , 0. , 0.26710379, 0.51184851,
0. , 0.26710379, 0.51184851, 0.26710379],
[0. , 0.46979139, 0.58028582, 0.38408524, 0. ,
0. , 0.38408524, 0. , 0.38408524]])
df = pd.DataFrame(X.toarray(), columns=tfidf.get_feature_names_out())
df
| and | document | first | is | one | second | the | third | this | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.000000 | 0.469791 | 0.580286 | 0.384085 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.384085 | 0.000000 | 0.384085 |
| 1 | 0.000000 | 0.687624 | 0.000000 | 0.281089 | 0.000000 | 0.538648 | 0.281089 | 0.000000 | 0.281089 |
| 2 | 0.511849 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.267104 | 0.511849 | 0.000000 | 0.267104 | 0.511849 | 0.267104 |
| 3 | 0.000000 | 0.469791 | 0.580286 | 0.384085 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.384085 | 0.000000 | 0.384085 |
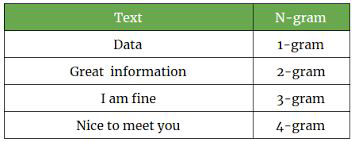
N-grams#
To model sequences of words… for example ice and cream make more sense as a 2-gram when they appear together
can be at word level or at character level
from nltk import ngrams
text
'Let us learn some NLP. NLP is amazing!'
n = 4
for i in range(1, n):
print(f"{i} gram\n")
ngram = ngrams(text.split(), i)
for gram in ngram:
print(gram)
print("-"*10)
1 gram
('Let',)
('us',)
('learn',)
('some',)
('NLP.',)
('NLP',)
('is',)
('amazing!',)
----------
2 gram
('Let', 'us')
('us', 'learn')
('learn', 'some')
('some', 'NLP.')
('NLP.', 'NLP')
('NLP', 'is')
('is', 'amazing!')
----------
3 gram
('Let', 'us', 'learn')
('us', 'learn', 'some')
('learn', 'some', 'NLP.')
('some', 'NLP.', 'NLP')
('NLP.', 'NLP', 'is')
('NLP', 'is', 'amazing!')
----------
Normalization#
[‘List’, ‘listed’, ‘lists’, ‘listing’, ‘listings’, ‘.’]
→ [‘list’, ‘listed’, ‘lists’, ‘listing’, ‘listings’, ‘.’]
Do we want to distinguish between “List” and “list”?
Sometimes we do: “White House” vs. “white house”
Notes: Normalization is the process of converting text data into a standardized form to reduce complexity and improve the efficiency of machine learning models. This can include lowercasing, stemming/lemmatization, …
Stemming#
[‘list’, ‘listed’, ‘lists’, ‘listing’, ‘listings’, ‘.’]
→ [‘list’, ‘list’, ‘list’, ‘list’, ‘list’, ‘.’]
Stemming reduces words to a shorter form, a form that might have no meaning.
Lemmatization#
[‘list’, ‘listed’, ‘lists’, ‘listing’, ‘listings’, ‘.’]
→ [‘list’, ‘listed’, ‘list’, ‘listing’, ‘listing’, ‘.’]
Lemmatization uses the language dictionary to get the base word of a word.
stemmer = nltk.PorterStemmer()
text = "We are learning how a stemmer works"
text1 = "People are running so fast."
tokenized_text = word_tokenize(text1)
stem = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in tokenized_text]
stem
['peopl', 'are', 'run', 'so', 'fast', '.']
lemmatizer = nltk.WordNetLemmatizer()
tokenized_text = word_tokenize(text1)
lemm = [lemmatizer.lemmatize(word) for word in tokenized_text]
lemm
['People', 'are', 'running', 'so', 'fast', '.']
Stemming or Lemmatization?#
It depends…
Stemming is faster
Lemmatization preserves more information
Stopwords#
some words do not provide meaningful information … they are not “content words”
the list of non-content words is language specific and corpus specific
What would you say are stop words in this text?
“Apple is looking at buying U.K. startup for $1 billion”
Stopwords#
some words do not provide meaningful information … they are not “content words”
the list of non-content words is language specific and corpus specific
What would you say are stop words in this text?
“Apple is looking at buying U.K. startup for $1 billion”
nltk.download("stopwords")
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
print(stopwords.words('english'))
['a', 'about', 'above', 'after', 'again', 'against', 'ain', 'all', 'am', 'an', 'and', 'any', 'are', 'aren', "aren't", 'as', 'at', 'be', 'because', 'been', 'before', 'being', 'below', 'between', 'both', 'but', 'by', 'can', 'couldn', "couldn't", 'd', 'did', 'didn', "didn't", 'do', 'does', 'doesn', "doesn't", 'doing', 'don', "don't", 'down', 'during', 'each', 'few', 'for', 'from', 'further', 'had', 'hadn', "hadn't", 'has', 'hasn', "hasn't", 'have', 'haven', "haven't", 'having', 'he', "he'd", "he'll", 'her', 'here', 'hers', 'herself', "he's", 'him', 'himself', 'his', 'how', 'i', "i'd", 'if', "i'll", "i'm", 'in', 'into', 'is', 'isn', "isn't", 'it', "it'd", "it'll", "it's", 'its', 'itself', "i've", 'just', 'll', 'm', 'ma', 'me', 'mightn', "mightn't", 'more', 'most', 'mustn', "mustn't", 'my', 'myself', 'needn', "needn't", 'no', 'nor', 'not', 'now', 'o', 'of', 'off', 'on', 'once', 'only', 'or', 'other', 'our', 'ours', 'ourselves', 'out', 'over', 'own', 're', 's', 'same', 'shan', "shan't", 'she', "she'd", "she'll", "she's", 'should', 'shouldn', "shouldn't", "should've", 'so', 'some', 'such', 't', 'than', 'that', "that'll", 'the', 'their', 'theirs', 'them', 'themselves', 'then', 'there', 'these', 'they', "they'd", "they'll", "they're", "they've", 'this', 'those', 'through', 'to', 'too', 'under', 'until', 'up', 've', 'very', 'was', 'wasn', "wasn't", 'we', "we'd", "we'll", "we're", 'were', 'weren', "weren't", "we've", 'what', 'when', 'where', 'which', 'while', 'who', 'whom', 'why', 'will', 'with', 'won', "won't", 'wouldn', "wouldn't", 'y', 'you', "you'd", "you'll", 'your', "you're", 'yours', 'yourself', 'yourselves', "you've"]
[nltk_data] Downloading package stopwords to /home/runner/nltk_data...
[nltk_data] Unzipping corpora/stopwords.zip.
So.. what do we do with all that?#
document similarity
text classification
…
Text similarity or Document Similarity#
Each document is a vector of features.
Similarity between documents is the similarity between vectors
Usage:
search engines: query to document
clustering of documents: document to document
Question & Answering platforms: query to query
Text classification#
You can use your favourite classifier with text
Logistic Regression provides nice baseline
AUC score as performance metric
Some applications:
spam detection
sentiment analysis
hate speech analysis
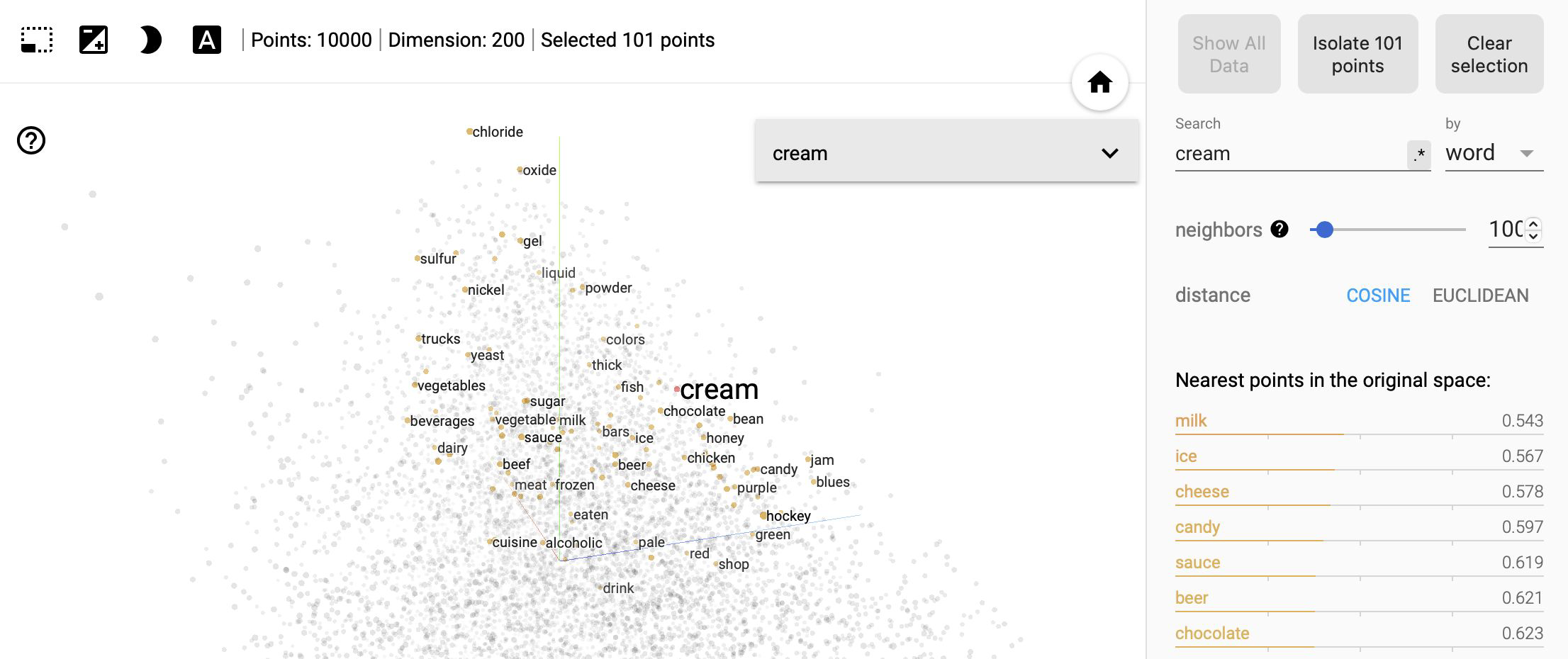
Word Embeddings#
Word Embeddings#
Represent feature space in smaller dimension
Similar words are near in embedding space
Trained by using neural networks
→ Use those trained weights as first layer in your NLP neural network.
Word similarity#
Is “St Pauli” more similar to:
De Wallen → Similar type
or
HSV → Similar topic?
Result depends on the context … or on the feature space / embedding you chose
Using Embeddings#
Relevant items for your task should be similar in the embedding space / i.e close to each other.
.

How do we get Word Embeddings#
How do we get Word Embeddings#
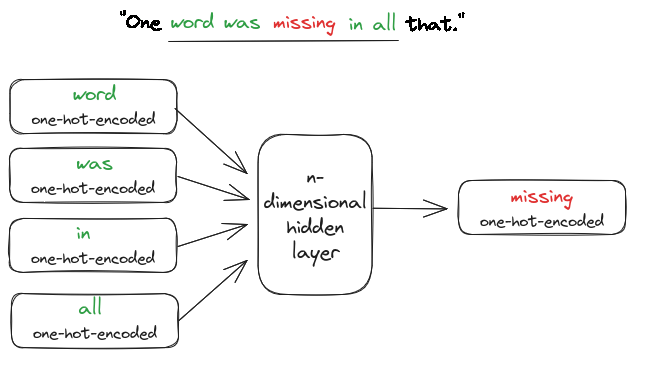
How do we get Word Embeddings#
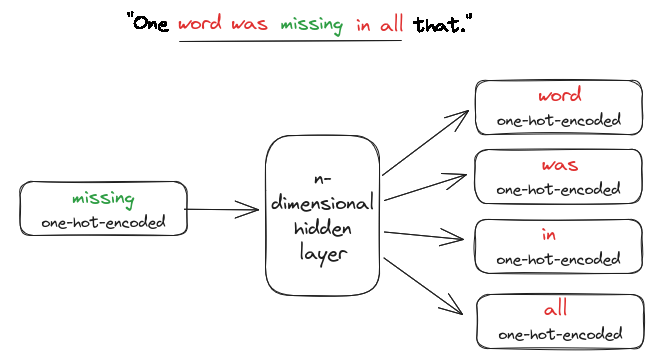
How do we get Word Embeddings#


Using pre-trained embeddings#
Most times you do not have enough data to get good word embeddings for your task, instead you can use pre-trained word embeddings.
There are different kinds of word embeddings:
static word embeddings: Word2vec (google), GloVe (Standford University), fastText (Facebook),
contextual word embeddings: ELMo, Bert (google), gpt-2/3/4 (openAI), …
example: pretrained word embeddings
Word Embeddings#
!pip install gensim
!pip install scipy==1.12
import gensim.downloader as api
## List available embeddings
info = api.info()
for model_name, model_data in sorted(info['models'].items()):
print(model_name)
__testing_word2vec-matrix-synopsis
conceptnet-numberbatch-17-06-300
fasttext-wiki-news-subwords-300
glove-twitter-100
glove-twitter-200
glove-twitter-25
glove-twitter-50
glove-wiki-gigaword-100
glove-wiki-gigaword-200
glove-wiki-gigaword-300
glove-wiki-gigaword-50
word2vec-google-news-300
word2vec-ruscorpora-300
# caveat: If you don't have enough RAM, this cell can crash your kernel
wv = api.load("word2vec-google-news-300")
glove = api.load("glove-twitter-100")
fasttext = api.load("fasttext-wiki-news-subwords-300")
from gensim.models import KeyedVectors
# Load the first 200,000 words from the downloaded file only instead
wv = KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_format('GoogleNews-vectors-negative300.bin.gz', binary=True, limit=200000)
wv.most_similar("coffee")
[('coffees', 0.721267819404602),
('gourmet_coffee', 0.7057086825370789),
('Coffee', 0.6900454759597778),
('o_joe', 0.6891065835952759),
('Starbucks_coffee', 0.6874972581863403),
('coffee_beans', 0.6749704480171204),
('latté', 0.664122462272644),
('cappuccino', 0.662549614906311),
('brewed_coffee', 0.6621608138084412),
('espresso', 0.6616826057434082)]
wv.get_vector("coffee")
array([-1.61132812e-01, -1.36718750e-01, -3.73046875e-01, 6.17187500e-01,
1.08398438e-01, 2.72216797e-02, 1.00097656e-01, -1.51367188e-01,
-1.66015625e-02, 3.80859375e-01, 6.54296875e-02, -1.31835938e-01,
2.53906250e-01, 9.08203125e-02, 2.86865234e-02, 2.53906250e-01,
-2.05078125e-01, 1.64062500e-01, 2.20703125e-01, -1.74804688e-01,
-2.01171875e-01, 1.30859375e-01, -3.22265625e-02, -2.41210938e-01,
-3.19824219e-02, 2.48046875e-01, -2.37304688e-01, 2.89062500e-01,
1.64794922e-02, 1.29394531e-02, 1.72119141e-02, -3.53515625e-01,
-1.66992188e-01, -5.90820312e-02, -2.81250000e-01, 9.94873047e-03,
-1.94091797e-02, -3.22265625e-01, 1.73339844e-02, -5.83496094e-02,
-2.59765625e-01, 1.42669678e-03, 5.81054688e-02, 1.13769531e-01,
-8.64257812e-02, 3.54003906e-02, -4.29687500e-01, 2.86865234e-03,
6.98852539e-03, 1.80664062e-01, -1.79687500e-01, 2.95410156e-02,
-1.56250000e-01, -2.08007812e-01, -9.08203125e-02, 4.15039062e-03,
1.07421875e-01, 3.12500000e-01, -1.04980469e-01, -3.24218750e-01,
-1.24023438e-01, -7.05718994e-04, -1.05957031e-01, 2.12890625e-01,
1.12304688e-01, -1.58203125e-01, -1.67968750e-01, -9.71679688e-02,
1.53320312e-01, -1.11328125e-01, 3.22265625e-01, 2.28515625e-01,
3.20312500e-01, -1.72119141e-02, -4.57031250e-01, 3.23486328e-03,
-1.76757812e-01, -5.00488281e-02, 3.05175781e-02, -2.75390625e-01,
-1.65039062e-01, -3.56445312e-02, 7.95898438e-02, 1.35742188e-01,
-8.64257812e-02, -7.32421875e-02, 1.36718750e-01, 2.33398438e-01,
7.95898438e-02, 1.32446289e-02, -4.71191406e-02, 1.01074219e-01,
2.37304688e-01, -1.81640625e-01, -2.14843750e-01, -1.65039062e-01,
-1.66015625e-02, -1.51367188e-01, 3.06640625e-01, -2.40234375e-01,
-2.29492188e-01, -1.29882812e-01, 8.97216797e-03, 1.97265625e-01,
7.47070312e-02, -1.64031982e-03, 1.54296875e-01, -6.80541992e-03,
-1.12304688e-01, -7.61718750e-02, -8.74023438e-02, -1.31835938e-01,
-2.94921875e-01, -2.46093750e-01, 6.15234375e-02, -1.23046875e-01,
-8.34960938e-02, -8.39843750e-02, -1.61132812e-02, -4.30297852e-03,
-4.05273438e-02, -2.84423828e-02, 1.36718750e-01, 2.13623047e-02,
-2.81250000e-01, 2.40234375e-01, -3.75976562e-02, -9.66796875e-02,
1.28906250e-01, 1.43554688e-01, -1.37695312e-01, -1.38549805e-02,
-4.12597656e-02, -4.51660156e-02, -3.75976562e-02, 1.89453125e-01,
5.32226562e-02, 1.17675781e-01, -8.25195312e-02, -1.56250000e-01,
1.47460938e-01, -2.63671875e-01, -2.79296875e-01, -4.31640625e-01,
-5.90820312e-02, 2.74658203e-03, 2.87109375e-01, -2.71606445e-03,
-2.46093750e-01, 2.74658203e-02, -9.08203125e-02, 6.54296875e-02,
-1.94335938e-01, -2.16064453e-02, 2.77343750e-01, 5.98144531e-02,
2.33154297e-02, -1.37695312e-01, -5.39062500e-01, -1.64794922e-02,
-1.25976562e-01, -1.36718750e-01, 3.02734375e-02, 2.50000000e-01,
5.53131104e-04, 1.36718750e-01, 2.96875000e-01, -5.10253906e-02,
9.08203125e-02, -2.39257812e-01, 1.35742188e-01, 1.11328125e-01,
1.96289062e-01, -1.54296875e-01, -3.37890625e-01, -3.36914062e-02,
-9.47265625e-02, -1.69921875e-01, -1.04003906e-01, 1.46484375e-01,
4.54101562e-02, -4.12109375e-01, -2.47070312e-01, -6.10351562e-03,
4.55078125e-01, -2.35595703e-02, 4.93164062e-02, 1.42578125e-01,
2.66113281e-02, 4.11987305e-03, -7.27539062e-02, 2.53906250e-02,
-3.39355469e-02, 7.91015625e-02, 2.87109375e-01, 3.88671875e-01,
-1.58691406e-02, -8.44726562e-02, -1.15722656e-01, -1.22558594e-01,
-1.02050781e-01, 1.32812500e-01, 2.21679688e-01, -2.03125000e-01,
7.91015625e-02, 1.69677734e-02, 2.16796875e-01, 2.33398438e-01,
-2.08984375e-01, -1.36718750e-01, -2.45117188e-01, 3.93066406e-02,
-1.80664062e-01, 1.37695312e-01, 1.50390625e-01, -3.90625000e-02,
-1.32812500e-01, 2.75878906e-02, -1.78710938e-01, 1.55273438e-01,
1.36718750e-01, -1.14257812e-01, -2.79296875e-01, -7.86132812e-02,
3.08593750e-01, -5.32226562e-02, -1.65039062e-01, 5.83496094e-02,
2.19726562e-01, -1.25000000e-01, 6.10351562e-02, -3.39355469e-02,
-3.16406250e-01, 2.14843750e-01, -4.12597656e-02, -1.94335938e-01,
7.76367188e-02, -5.21850586e-03, 6.93359375e-02, 2.18750000e-01,
1.71875000e-01, -1.97265625e-01, 1.07910156e-01, 8.25195312e-02,
3.39355469e-02, -1.15722656e-01, -2.02941895e-03, 4.83398438e-02,
1.50390625e-01, -2.73437500e-01, -9.61914062e-02, 3.39843750e-01,
2.98828125e-01, 1.32812500e-01, -3.68652344e-02, -3.08593750e-01,
2.94189453e-02, -1.31835938e-01, -7.12890625e-02, -2.57873535e-03,
-1.17187500e-01, 6.34765625e-03, -1.66992188e-01, 2.01171875e-01,
-1.33789062e-01, -1.77734375e-01, -1.09863281e-01, 5.06591797e-03,
-1.07910156e-01, -1.30859375e-01, -5.17578125e-02, 2.57812500e-01,
5.41992188e-02, -6.34765625e-03, 3.00598145e-03, 7.95898438e-02,
-2.37304688e-01, -8.05664062e-02, 6.07910156e-02, 9.27734375e-02,
1.65039062e-01, -1.22558594e-01, 1.88476562e-01, 2.50000000e-01,
-1.42578125e-01, -7.91015625e-02, -1.78710938e-01, 1.52343750e-01,
-7.76367188e-02, 2.42187500e-01, 2.56347656e-02, -1.26953125e-01,
-1.25000000e-01, -3.19824219e-02, -1.27929688e-01, 1.49414062e-01,
-1.34277344e-02, 6.59179688e-02, 2.17773438e-01, 2.02148438e-01],
dtype=float32)
glove.most_similar("coffee")
[('tea', 0.8275877237319946),
('beer', 0.7744594216346741),
('breakfast', 0.7694926261901855),
('coffe', 0.762207567691803),
('starbucks', 0.7606451511383057),
('food', 0.75710529088974),
('wine', 0.7540071606636047),
('drink', 0.7533924579620361),
('milk', 0.7433452010154724),
('cream', 0.7419354915618896)]
fasttext.most_similar("coffee")
[('coffees', 0.8029798269271851),
('coffeee', 0.7699174880981445),
('non-coffee', 0.7645688056945801),
('tea', 0.7583761215209961),
('coffe', 0.754230797290802),
('coffee-', 0.7451688647270203),
('cappuccino', 0.7182677388191223),
('coffee.', 0.7153727412223816),
('decaf', 0.7138857841491699),
('coffee-making', 0.7045937180519104)]
wv.distance("coffee", "tea")
# wv.distance("coffee","coffees")
0.43647074699401855
wv.distance("coffee", "onion")
0.8041959255933762
wv.most_similar(positive=["king", "woman"], negative=["man"])
[('queen', 0.7118192911148071),
('monarch', 0.6189674735069275),
('princess', 0.5902431011199951),
('crown_prince', 0.5499460697174072),
('prince', 0.5377321243286133),
('kings', 0.5236844420433044),
('Queen_Consort', 0.5235945582389832),
('queens', 0.5181134343147278),
('sultan', 0.5098593235015869),
('monarchy', 0.5087411403656006)]
wv.most_similar(positive=["restaurant", "coffee"], negative=["dinner"])
[('coffee_shop', 0.6624683141708374),
('Starbucks', 0.6141722202301025),
('gourmet_coffee', 0.6009524464607239),
('Starbucks_coffee', 0.5996598601341248),
('coffeehouse', 0.5934416651725769),
('cafe', 0.586820662021637),
('bakery', 0.5799906253814697),
('café', 0.571239709854126),
('coffee_beans', 0.566901683807373),
('espresso', 0.5581566691398621)]
wv.most_similar(positive=["Berlin", "France"], negative=["Germany"])
[('Paris', 0.7672389149665833),
('French', 0.6049168109893799),
('Parisian', 0.5810437202453613),
('Colombes', 0.5599984526634216),
('Hopital_Europeen_Georges_Pompidou', 0.5558906197547913),
('Melun', 0.551270067691803),
('Dinard', 0.5451847314834595),
('Brussels', 0.5420989990234375),
('Mairie_de', 0.533744752407074),
('Cagnes_sur_Mer', 0.5312464833259583)]
wv.doesnt_match(["sklearn","numpy","python","pandas"])
'pandas'
# find out which other methods there are and test their function
dir(wv)
['__class__',
'__contains__',
'__delattr__',
'__dict__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__getitem__',
'__getstate__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__init_subclass__',
'__le__',
'__len__',
'__lt__',
'__module__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__setattr__',
'__setitem__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__',
'__weakref__',
'_adapt_by_suffix',
'_load_specials',
'_log_evaluate_word_analogies',
'_save_specials',
'_smart_save',
'_upconvert_old_d2vkv',
'_upconvert_old_vocab',
'add_lifecycle_event',
'add_vector',
'add_vectors',
'allocate_vecattrs',
'closer_than',
'cosine_similarities',
'distance',
'distances',
'doesnt_match',
'evaluate_word_analogies',
'evaluate_word_pairs',
'expandos',
'fill_norms',
'get_index',
'get_mean_vector',
'get_normed_vectors',
'get_vecattr',
'get_vector',
'has_index_for',
'index2entity',
'index2word',
'index_to_key',
'init_sims',
'intersect_word2vec_format',
'key_to_index',
'lifecycle_events',
'load',
'load_word2vec_format',
'log_accuracy',
'log_evaluate_word_pairs',
'mapfile_path',
'most_similar',
'most_similar_cosmul',
'most_similar_to_given',
'n_similarity',
'next_index',
'norms',
'rank',
'rank_by_centrality',
'relative_cosine_similarity',
'resize_vectors',
'save',
'save_word2vec_format',
'set_vecattr',
'similar_by_key',
'similar_by_vector',
'similar_by_word',
'similarity',
'similarity_unseen_docs',
'sort_by_descending_frequency',
'unit_normalize_all',
'vector_size',
'vectors',
'vectors_for_all',
'vectors_norm',
'vocab',
'wmdistance',
'word_vec',
'words_closer_than']
Visualize Semantics with Graphs#
Hugging Face & Transformers#

Transformers#

Transformers#

Notes:
The encoder’s inputs first flow through a self-attention layer – a layer that helps the encoder look at other words in the input sentence as it encodes a specific word. The outputs of the self-attention layer are fed to a feed-forward neural network. The exact same feed-forward network is independently applied to each position.
The decoder has both those layers, but between them is an attention layer that helps the decoder focus on relevant parts of the input sentence
Transformers#

Notes:
What does “it” in this sentence refer to? Is it referring to the street or to the animal? It’s a simple question to a human, but not as simple to an algorithm.
When the model is processing the word “it”, self-attention allows it to associate “it” with “animal”.
As the model processes each word (each position in the input sequence), self attention allows it to look at other positions in the input sequence for clues that can help lead to a better encoding for this word.
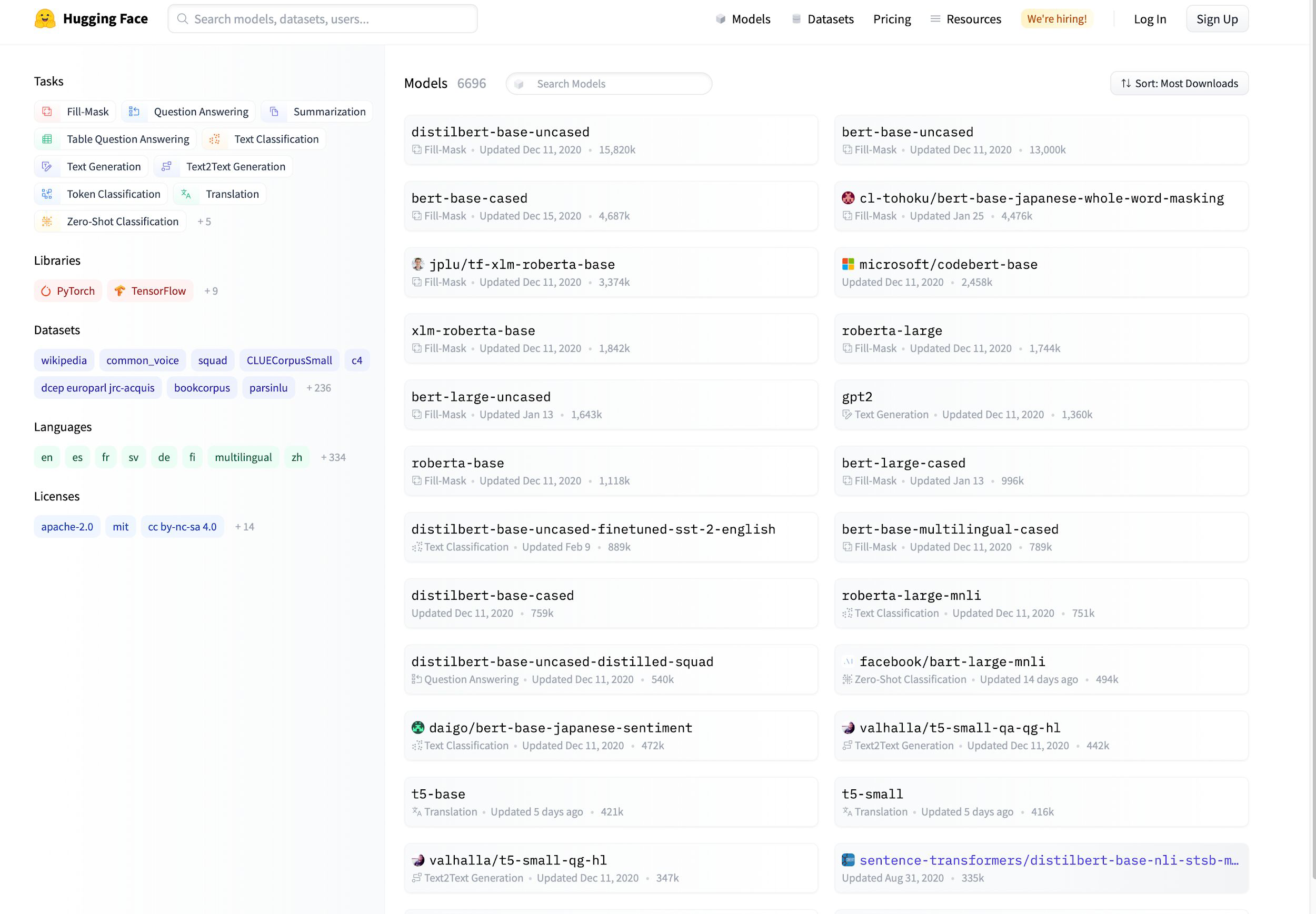
Hugging Face#
~ 15k pre trained NLP models on huggingface.co
Zero Shot Learning#
When you have little data.
Zero-shot learning (ZSL) is a problem setup in machine learning, where at test time, a learner observes samples from classes that were not observed during training, and needs to predict the class they belong to.
(see notebook 2 in workbooks)
Resources#
Sentiment Analysis with VADER [stand alone, using nltk]
